Stellantis’ ambitious plans to build 100,000 hydrogen-powered vehicles by 2030
According to several media reports, Stellantis is planning to produce 100,000 hydrogen-powered vehicles by 2030. Most of them could be light commercial vehicles. Stellantis will have eight fuel cell hydrogen versions of mid-size and large vans produced in-house, in both France and Poland.

According to several media reports, Stellantis is planning to produce 100,000 hydrogen-powered vehicles by 2030. Most of them could be light commercial vehicles. It’s quite an impressive figure, indeed. We wrote about the Group’s will to start producing hydrogen-powered vans at the company’s plants of Hordain (France) and Gliwice (Poland) under the Stellantis ProOne brand.
“This year, we are starting production of larger vehicles in Poland, and development in North America will follow quickly – especially for the fuel cell version of the large Ram 5500”, said Jean-Michel Billig, head of the Group’s hydrogen programme, as reported by Electrive. “In the coming decade, we expect a significant market share for this technology, which could be up to 40 per cent for commercial vehicles”, he added.
Eight hydrogen-powered LCV models in the Stellantis portfolio
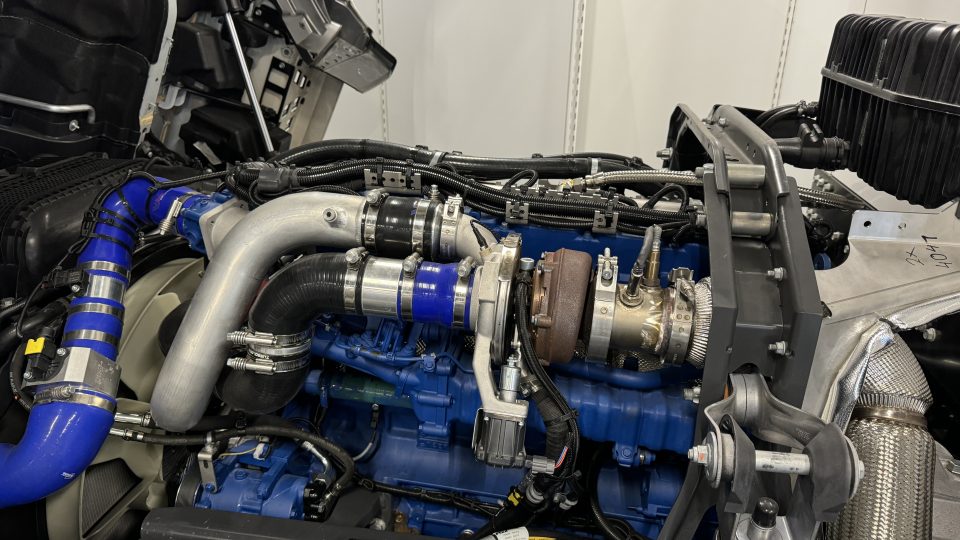
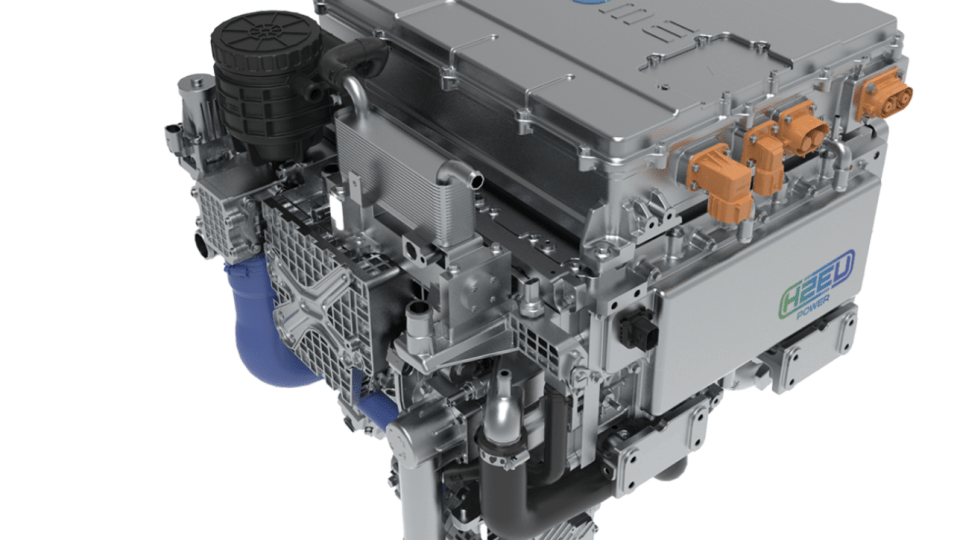
The fuel cell versions of the commercial vans build on the technology used in the zero-emission BEV variants of the vehicles, with the added advantages of short refueling times and no sacrifice of payload capability. For the mid-size vans, a second generation of the fuel cell system delivers a segment record range of up to 400 km and refueling time of less than four minutes. For the large vans, the addition of fuel cell technology brings range capability of up to 500 km and refueling time of just five minutes.
Stellantis will have eight fuel cell hydrogen versions of mid-size and large vans produced in-house: Citroën ë-Jumpy and ë-Jumper, Fiat Professional E-Scudo and E-Ducato, Opel Vivaro and Movano, and Peugeot E-Expert and E-Boxer.